-
Your Chance To
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Description
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Getting There
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Red Tape
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Are You Ready?
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Tips
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
Cellular Network:
Yes (Guided Tours)
Mobile Internet:
Yes (settalite phone )
1953
May 29
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit
At 11:30 a.m. on May 29, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay, a Sherpa of Nepal, become the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, which at 29,035 feet above sea level is the highest point on earth. The two, part of a British expedition, made their final assault on the summit after spending a fitful night at 27,900 feet. News of their achievement broke around the world on June 2, the day of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, and Britons hailed it as a good omen for their country’s future.
Mount Everest sits on the crest of the Great Himalayas in Asia, lying on the border between Nepal and Tibet. Called Chomo-Lungma, or “Mother Goddess of the Land,” by the Tibetans, the English named the mountain after Sir George Everest, a 19th-century British surveyor of South Asia. The summit of Everest reaches two-thirds of the way through the air of the earth’s atmosphere–at about the cruising altitude of jet airliners–and oxygen levels there are very low, temperatures are extremely cold, and weather is unpredictable and dangerous.
The first recorded attempt to climb Everest was made in 1921 by a British expedition that trekked 400 difficult miles across the Tibetan plateau to the foot of the great mountain. A raging storm forced them to abort their ascent, but the mountaineers, among them George Leigh Mallory, had seen what appeared to be a feasible route up the peak. It was Mallory who quipped when later asked by a journalist why he wanted to climb Everest, “Because it’s there.”
A second British expedition, featuring Mallory, returned in 1922, and climbers George Finch and Geoffrey Bruce reached an impressive height of more than 27,000 feet. In another attempt made by Mallory that year, seven Sherpa porters were killed in an avalanche. (The Sherpas, native to the Khumbu region, have long played an essential support role in Himalayan climbs and treks because of their strength and ability to endure the high altitudes.) In 1924, a third Everest expedition was launched by the British, and climber Edward Norton reached an elevation of 28,128 feet, 900 vertical feet short of the summit, without using artificial oxygen. Four days later, Mallory and Andrew Irvine launched a summit assault and were never seen alive again. In 1999, Mallory’s largely preserved body was found high on Everest–he had suffered numerous broken bones in a fall. Whether or not he or Irvine reached the summit remains a mystery.
Several more unsuccessful summit attempts were made via Tibet’s Northeast Ridge route, and after World War II Tibet was closed to foreigners. In 1949, Nepal opened its door to the outside world, and in 1950 and 1951 British expeditions made exploratory climbs up the Southeast Ridge route. In 1952, a Swiss expedition navigated the treacherous Khumbu Icefall in the first real summit attempt. Two climbers, Raymond Lambert and Tenzing Norgay, reached 28,210 feet, just below the South Summit, but had to turn back for want of supplies.
Shocked by the near-success of the Swiss expedition, a large British expedition was organized for 1953 under the command of Colonel John Hunt. In addition to the best British climbers and such highly experienced Sherpas as Tenzing Norgay, the expedition enlisted talent from the British Commonwealth, such as New Zealanders George Lowe and Edmund Hillary, the latter of whom worked as a beekeeper when not climbing mountains. Members of the expedition were equipped with specially insulated boots and clothing, portable radio equipment, and open- and closed-circuit oxygen systems.
Setting up a series of camps, the expedition pushed its way up the mountain in April and May 1953. A new passage was forged through the Khumbu Icefall, and the climbers made their way up the Western Cwm, across the Lhotse Face, and to the South Col, at about 26,000 feet. On May 26, Charles Evans and Tom Bourdillon launched the first assault on the summit and came within 300 feet of the top of Everest before having to turn back because one of their oxygen sets was malfunctioning.
On May 28, Tenzing and Hillary set out, setting up high camp at 27,900 feet. After a freezing, sleepless night, the pair plodded on, reaching the South Summit by 9 a.m. and a steep rocky step, some 40 feet high, about an hour later. Wedging himself in a crack in the face, Hillary inched himself up what was thereafter known as the Hillary Step. Hillary threw down a rope, and Norgay followed. At about 11:30 a.m., the climbers arrived at the top of the world.
News of the success was rushed by runner from the expedition’s base camp to the radio post at Namche Bazar, and then sent by coded message to London, where Queen Elizabeth II learned of the achievement on June 1, the eve of her coronation. The next day, the news broke around the world. Later that year, Hillary and Hunt were knighted by the queen. Norgay, because he was not a citizen of a Commonwealth nation, received the lesser British Empire Medal.
Since Hillary and Norgay’s historic climb, numerous expeditions have made their way up to Everest’s summit. In 1960, a Chinese expedition was the first to conquer the mountain from the Tibetan side, and in 1963 James Whittaker became the first American to top Everest. In 1975, Tabei Junko of Japan became the first woman to reach the summit. Three years later, Reinhold Messner of Italy and Peter Habeler of Austria achieved what had been previously thought impossible: climbing to the Everest summit without oxygen. More than 300 climbers have died attempting to summit the mountain.
Everest’s deadliest day occurred on April 25, 2015, when 19 people were killed in an avalanche at base camp following a 7.8 earthquake, which killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000 in Nepal.
A major tragedy occurred in 1996 when eight climbers died after being caught in a blizzard high on the slopes in an incident made famous by Jon Krakauer’s book Into Thin Air. Krakauer's book did nothing to stem the tide of people willing to shell out tens of thousands of dollars for a chance to summit Earth’s highest mountain. Traffic jams have been reported near the top, and a fistfight broke out in 2013 between three European climbers and more than 100 Sherpas, over what the guides deemed to be rude and dangerous behavior during an attempted ascent. Meanwhile, the deaths keep coming, including over 10 in 2019.
-
Parameters
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
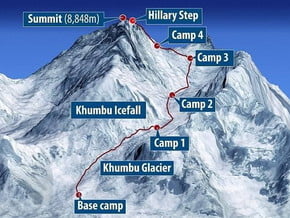
| Base Camp Elevation: |
5 500 m / 18 045 ft |
| Summit Camp Elevation: |
7 450 m / 24 442 ft |
| Accommodation in Base Camp: |
Both - huts and tents |
| Accommodation above Base Camp: |
Both - huts and tents |
| Number of Camps: |
4 |
| Avg. Cost: |
33 500 USD |
| Age Restrictions: |
At least 21 years old |
| Soloing: |
Yes |
| Descent Route: |
Same |
| Specify descent time: |
10 Hour(s) |
-
Key Points
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
|
Name (Elevation)
|
Description
|
Base Camp
5 500 m / 18 045 tf |
Everest Base Camp |
-
Agencies
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
Guided Tours
-
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd.
- WE ORGANIZE : EXPEDITION - 6000M-7000M to 8000M / PEAK CLIMBING / TREKKING AND TOURS
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. welcomes all the interested parties and agents to join us as our travel partner. By partnering with Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. you will enjoy attractive incentives, well established vendor relationship, marketing opportunities, extensive travel resources and services and many more opportunity in the industry. Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition from Nepal we are looking for B2B travel and Expedition, Peak Climbing and trekking or commission basis & let’s exchange document, just send your contracted rate via email:info@asianadventurenepal.com
If you have traveled with us already in the past then you already have known us or if you are traveling with us for the first time then you will know about us once you complete your trip with us and the difference to travel with us as the Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition’ is a local based expedition, peak climbing, trekking, tour, travel and outdoor company. With over a decade of extensive experience in Nepal’s tourism industry fully owned & operated by Nepalese professionals has led tourist visitors on adventure holidays through some of the most rugged and remote mountainous regions of the Himalayan country of Nepal, Tibet, Bhutan, Darjeeling, Sikkim, India, Pakistan.
We are expert seasoned outdoor operator that offers some of the most thrilling experiences in the raw wilderness across some of the most remote & beautiful terrain in the world, our ‘Pure adventure’ trips cut across of-the-beaten-trails. We have behind us over a decade of experience in escorted ventures that cover some of the most mountaineering adventurous spots on the planet…we’ve trekked some of the toughest terrain on earth and despite the blood, sweat and tears, we’ve experienced on the way, we did not hesitate to go the extra mile to ensure that our guests were always safe and enjoyed the trails & landscapes…even in areas without human settlements…but raw beauty that left our guests gasping for breath every yard they trekked through…we reckoned this is what true holidays were made of…holidays that became lifelong stories for the generations on the way…heading back home with exclusive Himalayan pictures hung in some of the most favorite rooms at home…
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. is a leading dedicated professional Mountaineering Expedition Company registered under the Nepal Government as Mountaineering Expeditions service provider Company in the south Asia. It has also been affiliated with many travel and tourism related associations. The company was founded by professional and experienced young and enthusiastic professionals. We have clients from all around the world including many famous mountaineers and corporate houses have already used our services. We are also pleased to have won many awards for our contribution in mountaineering and national economy. We have well established team of professionals in our business having mixture of experience in this field which makes all our trips a success. So, having decades of experience in mountaineering expedition we at Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition are confident that our clients receive accurate, reliable and efficient service for any mountaineering expedition requirements in the Himalayas. We give utmost priority for client safety and success maintaining an eco-friendly mountaineering expedition.
Our Company supporters:
Our programs across Nepal, Tibet, Bhutan Darjeeling and Sikkim are led by talented and professional tour and trekking guides who not only know their jobs well but also enjoy it thoroughly, Our guides are well versed on the trials that come on the trails and the rivers and possess extensive knowledge on the destinations you choose, the guides enlisted on our payrolls are highly trained & most of them were born on the mountains & are highly experienced and can save lives if and when required. We are proud of them for one aspect in their difficult line of work. They simply love their jobs and take much pleasure in serving their fellow beings.
Why it’s important that you need to travel with Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. ?
A real pragmatic holiday experience is always at the heart of all our adventures an adventure travel holiday is about what you learnt from your holidays. Whether viewing Everest the world’s highest mountain from a trek to Base Camp of Everest, witnessing the magical aura of the Annapurna Himalayas or enjoying in the street festivities party in Kathmandu or sitting amongst the village folks in some remote outpost below towering mountains. Our aim to capture the spirit of this experience on our adventure journeys into the wild. Our wilderness tours are about discovery personal achievement and companionship.
They will test your patience inspire your emotions and flirt with all your senses. Traveling the paths less trodden, visiting remote communities, old sites and awesome landscapes are one and the same when planning your holidays with us it is about learning about experiencing and there is fun and it is also about knowing yourself and discovering yourself.
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. are extremely committed to preserving the natural environment when we plan your holidays and make doubly sure that the area is kept clean on the conclusion of our programs. Our guides and assistance are well equipped and geared to providing you flawless services. Always keeping in mind at all times first and foremost; your safety and protection throughout your program. We do not make camp fires and we strongly discourage trekkers from buying wood-fueled hot showers in lodges along the trail.
Our considerate programs ensure. We ‘give approximately back’ to our people in the areas that we travel. Our current initiative is project called ‘Practical Tourism’’ – ‘Keep the Mountains Clean – Give back to the Community’’. The concept behind our Practical Travel Program is based on the culture of “travel with a purpose”. It is a range of small group adventures, each about two weeks in length. Whereby participants commit four to five days of their holiday to making a difference to a community in need.
When we started Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition Pvt. Ltd. is one of the fastest growing tour and Trekking company in Nepal. It was our vision to provide our guests with extraordinary holiday experiences and despite our having come a long way today. Our approach to travel remains the same and we are just as passionate like the way we were in the very beginning. Come and Share this passion of ours and embark on the journey of a lifetime. Whether you’re one of our past travelers or totally new to us.
We invite you to look through the array of small group journey & itineraries. Featured on our highly informative website view our true to life Itineraries, when we tell you about a bird or some unique specimen of a flower or if it’s a shrub or a particular ridge or some green hillock. It’s there for real just the way you read about it.
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition invites you to Nepal go tell it on the mountains…in the cities & everywhere. Because it’s an invitation to another world you didn’t know a world that ensures your freedom a world that tells you are born free as free as the grass grows as free as the wind blows across the mighty Himalayas of lovely Nepal.
Our vision:
“Your dream into reality, Escorted Nepalese Adventure Company “Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition”. Come and join us for any individual to Extreme adventurous group trips. “What we are all for”. Traveling is not only about airplanes, car rentals, hotels and walking etc. moreover. The traveling is about discovering the new worlds and yourself. Experiencing new destinations, people cultures, landscapes, lifestyle, meeting new people and brings lots of memories and knowledge to home share with the families, friends and beloved one.
Asiana Nepal Treks & Expedition have vision to become number one wholesale travel, Expedition, Peak Climbing, tours, trekking company by providing variety of services including: trekking in Nepal, 4 season outdoor breaks, adventure sports, cultural tours, historical excursions, classic countryside walking treks on off-the-beat trails, wild river rafting, remote wilderness trek, overland tours, visiting exclusive heritage sites, thrilling mountain bikes educational tours, spiritual tours, cozy home stays, practical volunteering, unique jungle safaris, domestic and international ticketing and reliable and safe transportation services throughout the Himalayas of Nepal, Bhutan and Tibet to discover these parts of the world.
Our special NO FRILLS prices don’t have any hidden costs and can cope with any level of tourists that even extends to the budget and shoe-string backpacker & the discerning traveler from any corner of the globe.
Our Mission:
Our mission is to provide first hand trekking and hiking, sightseeing and tours, climbing and expedition, wildlife and safaris , rafting and river adventures, outdoor activities and all the travel related service at competitive price within its destinations (Nepal, Tibet, Bhutan, Darjeeling, Sikkim, India and Pakistan) to any level of tourist from any corner of the globe with continued commitment to ensure that we have a lasting positive effect while our tourism can be a real help to local communities generating income, positive cultural exchanges and protecting the natural environment.
-
GPS-Tracks
-
Did You Know
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates
Highest access: 8,848m (29,029ft)
First Ascent: May 29, 1953 Edmund Hillary & Tenzing Norgey Sherpa
Duration: 64 Days, Group Size: 08-10 persons per group, Co-ordinates: 27°59'17'' N / 86°55'31'' E
Location: Nepal/Tibet border, Country: Nepal, Airport: Kathmandu Airport
Departure From: Kathmandu Airport, Grade: Challenging, Accommodation: Three star to five star as request
Meals: B/B plan in Kathmandu & B, I, D during trekking and climbing
Transportation: vehicle and domestic flight, Best season: Spring Season (April, May)
Major Activity: Trekking/Mountaineering, Include Activity: Trekking/Mountaineering
Culture: Sherpa and Tamang, Mode of Travel: Tea House/Camping,
Climbing route: South East Ridge (Normal route)
Himalayan sights: Lhotse, Makalu, Ama Dablam, Cho-Oyu
... Read more
-
References
Edit •
Add / Share you knowledge with mates